Java Database Connectivity
- JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. It is a step by step procedure to communicate with the database from the Java application in order to perform database operation. Basically, JDBC is an Application Programming Interface (API) that makes it possible to standardize and simplify the process of connecting Java applications to a database.
- DBC is considered to be a part of Java platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) uses the Structured Query Languages (SQL) for performing different database queries like access, storage, update or delete.
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) supports Structured Query Language (SQL). Since Java is a platform independent programming language which runs on most platforms, JDBC helps to write a single database application which can run on different platforms and interact with different Database Management Systems.
Architecture of JDBC
JDBC Driver
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
1. JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
2. Native-API driver (partially java driver)
3. Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
4. Thin driver (fully java driver)
- JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver/Type-1 Driver: There are some databases which provide ODBC driver to connect their databases. Here, ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of thin driver.
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
1. JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
2. Native-API driver (partially java driver)
3. Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
4. Thin driver (fully java driver)
- JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver/Type-1 Driver: There are some databases which provide ODBC driver to connect their databases. Here, ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of thin driver.
Advantage: 1) Performance is upgraded compared to JDBC-OBDC/Type 1 driver.
Disadvantage: 2) Need to install Native API driver on each of the client machine.
- Native-API driver:-
The Native API driver uses the client -side libraries of the database. This driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. In order to interact with different database, this driver needs their local API, that's why data transfer is much more secure as compared to type-1 driver.
- Driver needs to be installed separately in individual client machines
- The Vendor client library needs to be installed on client machine.
- Type-2 driver isn’t written in java, that’s why it isn’t a portable driver
- It is a database dependent driver.
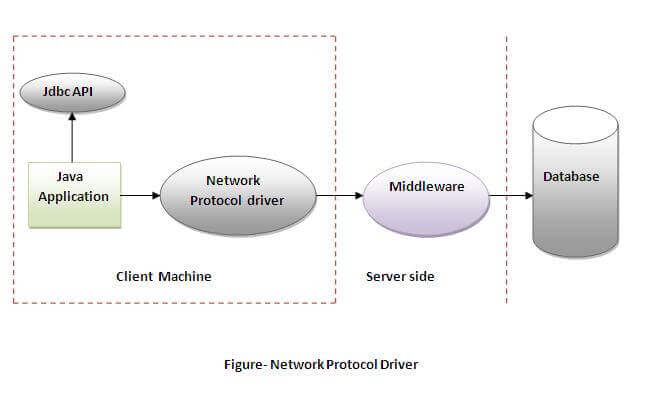
- Network Protocol driver
The Network Protocol driver uses middleware (application server) that converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol. It is fully written in java.
Advantage:
- No client side library is required because of application server that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing, logging etc.
Disadvantages:
- Network support is required on client machine.
- Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
- Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly because it requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
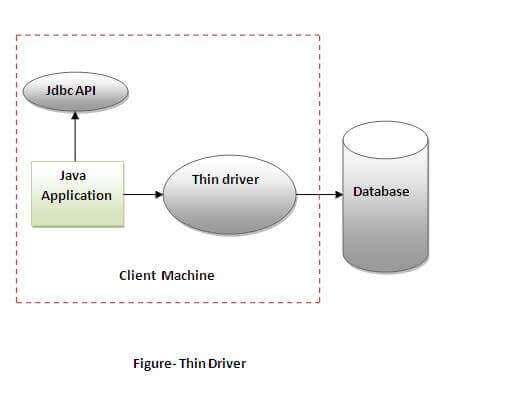
- Thin Driver :-
- The thin driver converts JDBC calls directly into the vendor-specific database protocol. That is why it is known as thin driver. It is fully written in Java language
Advantage:
- Better performance than all other drivers.
- No software is required at client side or server side.
Disadvantage:
- Drivers depend on the Database.
JDBC components:
- DriverManager: DriverManager is a class which manages all the database drivers. The DriverManager is used to load the specific database drivers in an application to establish a connection with the database.
- Driver: Driver is the interface which manages the communications happening between the application and the database server.
- Connection: Connection is an interface which contains methods for contacting the database.
- Statement: Statement is an interface that creates an object to submit SQL queries or statements to the database.
- ResultSet: ResultSet contains the results that are retrieved from the database after the execution of SQL statements or queries.
- SQLException: SQLException class is used to handle any of the errors that occur in a database application.
Figure- Java Database
Connectivity
There are 5 steps to connect any java application with the database using JDBC. These steps are as follows:-
- Load
the driver class: Load
the JDBC driver class into Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The forName() method
of class is used to load the driver class.
- Establish
the connection: Here a connection between a
Java program with the database is established using getConnection() method
provided by DriverManager class.
- Create
statement: In this step, the statement object is created
using createStatement() method of connection interface.
This statement object is used to interact with the database.
- Execute
query: This step involves executing queries to the
database and getting the output by using executeQuery() method
Statement interface.
- Close
the connection: The close() method
provided by Connection interface is used to close the connection.
There are three types of Statement available in Statement class:-
- Statement
- PreparedStatement
- CallableStatement
- Types of Statements:-
- Statement:- This represent a simple sql/mysql statement . Statement
stmt=con.createStatement();
- PreparedStatement :- This represent precompiled sql/my sql statement which allows improved
performance. It allows to execute the query multiple times and we can set
the values according to our need. PreparedStatement
psmt=con.prepareStatement();
- CallableStatement :- This allows the access of stored procedures; that are stored on the
database. CallableStatement csmt=con.prepareCall();
- Advantages of Java Database Connectivity :-
1. JDBC itself creates XML format of data from the database automatically
2. JDBC supports modules
3. JDBC provides better security
4. JDBC completely supports query and stored procedure
5. JDBC supports both types of processing i.e. Synchronous and Asynchronous processing
6. JDBC does not require content conversion.
Difference between JDBC and ODBC drivers:
As we know, that Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an API for Java Programming Language used to connect the Java application to the database, whereas Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface used for connecting application and database.
| JDBC | ODBC |
| JDBC is platform independent. | ODBC is platform dependent. |
| Code written in JDBC is easy to understand. | Code written in ODBC is complex to understand. |
| JDBC can be used only with Java programming language. | ODBC can be used in C, C++, Java programming language. |





very good
ReplyDeleteNice blog
ReplyDeleteHelpful Information 👍
ReplyDeleteNice info !!
ReplyDeleteNicely explained
ReplyDeleteThanks
DeleteGreat information. 🔥
ReplyDeletethanks for appreciation
DeleteNice blog
ReplyDeleteGreat Information.
ReplyDeleteVery Nice
Well done Ramkrishna . Keep it up bro 👍
ReplyDeleteWell done Ramkrishna . Keep it up bro 👍
ReplyDeleteWell done Ramkrishna . Keep it up bro 👍
ReplyDeleteGreat info
ReplyDeleteNice blog
ReplyDeletePerfectly explained 👌
ReplyDeleteWell Explained concepts👍
ReplyDeleteInformative blog👍🏻
ReplyDeleteNice Great Information .
ReplyDelete